Tax season got you scratching your head? Don’t worry, Form 16 is here to save the day. Think of it as your tax-time superhero, breaking down your income and TDS so filing your ITR feels less like a puzzle and more like a win. Let’s decode the meaning of Form 16 and make tax filing a breeze.

What Is Form 16 and Why Is It Important?
Form 16 is an official certificate issued by an employer to an employee, serving as a detailed summary of the salary paid and the tax deducted at source (TDS) during a financial year. It is a critical document for salaried individuals, as it provides evidence that the employer has deducted and deposited the applicable income tax with the government on behalf of the employee. As such, Form 16 acts as a comprehensive record that helps employees prepare and file their Income Tax Returns (ITR) with clarity and compliance.
It is divided into two parts:
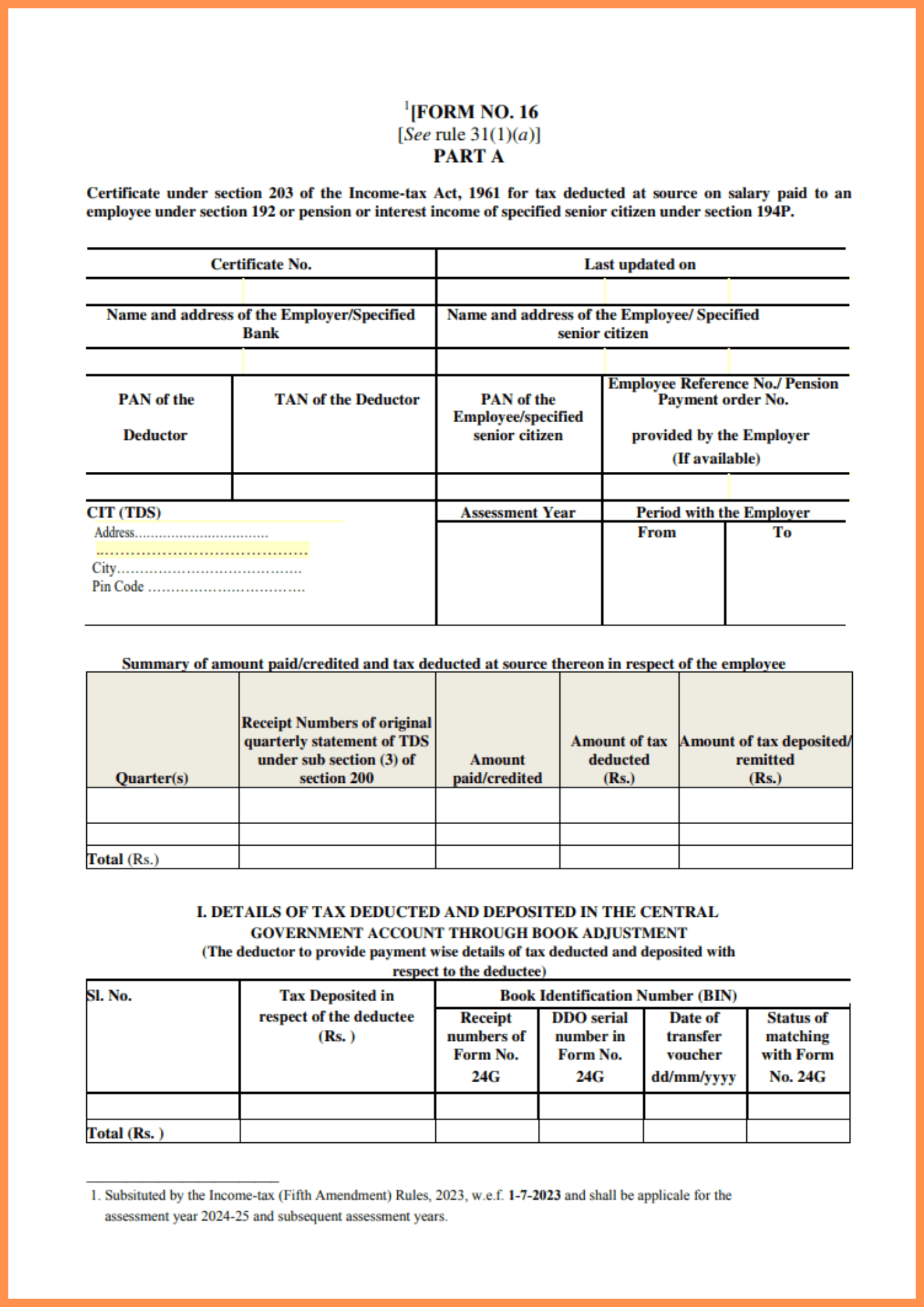
Part A - TDS Summary
In this section, you will find the employer’s PAN and the employee’s PAN, which help link the tax deduction records to both the employer and employee. Most importantly, part A shows the amount of tax deducted and deposited with the income tax department, providing a clear picture of the TDS payments made on your behalf.
Part B - Income and Deduction Details
Part B provides a detailed breakdown of your total income, starting with your gross salary for the year. It then shows how your taxable income is calculated after deductions, such as those under Section 80C.
How to Use Form 16 While Filing Your ITR
Wondering how to fill Form 16 while filing your ITR? Follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Download and Access Form 16
Your employer is required to issue this form by 31st May of the assessment year. You may receive it via email, the company HR portal, or directly from the HR/accounts department. Ensure that both Part A and Part B are provided.
Step 2: Verify Details in Part A
Form 16 Part A includes:
Your name and PAN
Employer’s name, PAN
Assessment year
Quarterly details of TDS deducted and deposited with the Income Tax Department
What to check:
Your PAN is correct.
The TDS amounts match your salary slips.
TDS entries match with Form 26AS (available on the Income Tax Portal).
If there are mismatches or errors, contact your employer for rectification.

Step 3: Cross-Verify Part B Salary and Deduction Details
Part B contains:
Breakdown of salary income
Exemptions (like HRA, LTA, standard deduction)
Deductions claimed under sections such as 80C (e.g., LIC, PPF), 80D (health insurance), 80E (education loan interest), etc.
Net taxable income
Total tax payable or refundable
What to check:
All claimed deductions match your investment proofs and actual savings.
Salary figures match your payslips and employment records.
Exemptions are correctly calculated.
Step 4: Use Form 16 for ITR Filing
Log in to the Income Tax Portal and fill in the details from Form 16 in the ITR form. The income and tax deducted sections should be accurately filled out using the figures provided in the form. Under the “Tax Details” tab, enter TDS amounts from Part A and make sure the employer TAN and TDS deposited match the form.
Step 5: Submit and E-Verify Your ITR
Review your return summary carefully using a comprehensive income tax filing resource to ensure accuracy.
Click Submit.
E-verify your return via Aadhaar OTP, Net Banking, or other options provided.
Without e-verification, your return will not be processed.
Key Components of Form 16 You Need to Understand
Part A: Employer-Provided TDS Breakdown
Part A is focused on tax deducted at source (TDS) from your salary and deposited with the Income Tax Department. It is generated and validated through the TRACES portal (TDS Reconciliation Analysis and Correction Enabling System), ensuring the authenticity of TDS records.
Here’s what Part A includes:
Name and Address of the Employer and Employee
PAN of the Employee and Employer
TAN of the Employer
Summary of TDS Deducted and Deposited
Assessment Year
Why It’s Important:
Part A proves that tax was deducted from your income and deposited with the authorities. Always cross-check these TDS amounts with Form 26AS (available on the income tax portal) to ensure consistency.
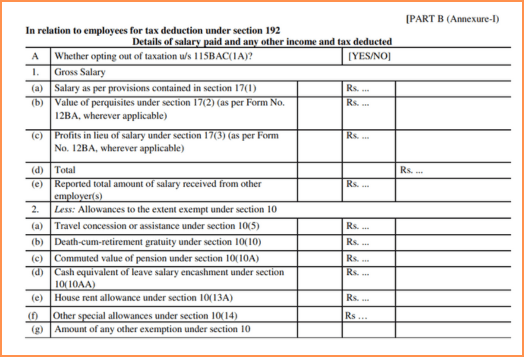
Part B: Detailed Salary Income and Tax Exemptions
Part B is prepared by your employer, but TRACES does not issue it. This section provides a full breakdown of your salary income, tax exemptions, deductions, and the tax payable or refund.
Here’s what you’ll find in Part B:
Gross Salary
Exemptions Under Section 10
Net Salary / Taxable Salary
Deductions Under Chapter VI-A (e.g., Sections 80C, 80D, 80G, etc.)
Total Taxable Income
Tax Liability and Rebate (if any)
Tax Already Deducted and Final Tax Payable or Refundable
Why It’s Important:
This section is where most users get confused while trying to fill in Form 16 details in their ITR. Every deduction and exemption listed here plays a vital role in reducing your tax liability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Form 16 While Filing ITR
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) using Form 16? While it simplifies the process, certain common errors can lead to mismatches, delays, or even notices from the Income Tax Department. Here’s how to avoid them:
1. Mismatch in TDS Amounts
It’s important to ensure that the TDS figures mentioned in Part A match your monthly salary slips and Form 26AS, which you can verify using proven tax filing strategies. If there’s a mismatch, it could indicate that your employer hasn’t deposited the TDS properly or reported it incorrectly. Always cross-check these amounts.
2. Missing Exemptions and Deductions
Part B includes salary details, tax exemptions (like HRA, LTA), and deductions under sections like 80C, 80D, etc. Ensure that:
All the investments and expenses you've declared (such as LIC, PPF, or health insurance) are reflected.
Exemptions such as standard deduction, HRA, or LTA are properly calculated.
Omitting eligible deductions could lead to a higher tax liability than necessary.
3. Incorrect PAN Details
An incorrect Permanent Account Number (PAN) in Form 16 or in your ITR can cause serious problems. Your TDS may not reflect correctly in the tax portal, and it may delay your ITR processing or result in failed e-verification. Check that your PAN is correctly mentioned in both forms.
Tip: When filling out your ITR, keep both Form 16 and Form 26AS open side by side to cross-verify every detail accurately.

Why Understanding Form 16 Is Key to Hassle-Free ITR Filing
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) doesn't need to be complicated, especially when you understand the Form 16 meaning and how to use it effectively. This important TDS certificate issued by your employer summarises your salary income, tax deductions, and exemptions for the financial year. By carefully reviewing Part A and Part B, verifying your personal details and deductions, you can avoid common errors and even maximise your tax savings.
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional advice or guidance. For personalised recommendations or specific concerns, please consult a certified professional.