The high-protein diet trend is hard to ignore, permeating social media, conversations, and grocery aisles. Its popularity stems from its benefits for muscle building, weight management, and overall health, with various foods like bars and shakes now widely available. But is the hype justified? Let’s delve into the advantages of a high-protein diet and see if it truly lives up to its reputation.
What is a High-protein Diet?
At its core, a protein-rich diet prioritizes protein over other macronutrients like carbs and fats. Typically, it involves consuming 20-30% (or more) of your daily calories from protein sources. Whether you’re feasting on chicken breasts, devouring chickpeas, or chugging a protein shake, the goal is to give your body a steady stream of this essential nutrient.
Why are high-protein diets so popular?
The appeal of protein-rich diets boils down to three big wins:
Muscle building: Protein provides the building blocks (amino acids) your muscles need to repair and grow stronger after workouts.
Weight loss and satiety: Protein keeps you fuller for longer, helping curb cravings and support sustainable weight loss.
Versatility: With so many high-protein foods to choose from, it’s easier than ever to make protein-rich meals you actually enjoy.
Benefits of High-protein Diets
Ready to take your health goals to the next level? Here’s how a diet with high protein helps you reach your goals.
Muscle building and recovery
When you exercise, especially during resistance training, your muscles experience tiny tears. These microtears are a good thing–they're how your muscles grow stronger. But they need the right fuel to recover, and that’s where protein comes in.
Protein provides amino acids, the building blocks of muscle, which repair and rebuild these tears. This makes diets with high protein indispensable for anyone who builds muscle or improves overall strength. Research shows that consuming protein-rich meals within an hour after a workout can significantly enhance muscle recovery and growth.
Weight management and metabolism
High-protein diets aren’t just about getting muscular; they’re a powerful ally for weight management. Protein takes longer to digest than carbs or fats, which means it keeps you feeling satisfied longer. This reduces the temptation to snack or overeat, making it easier to stick to your calorie goals.
Additionally, digesting protein actually burns more calories than processing other macronutrients, a phenomenon known as the thermic effect of food. So, while you’re enjoying that grilled chicken or creamy Greek yoghurt, your metabolism gets a little extra boost.
Additional health benefits
Protein doesn’t just power your muscles; it supports nearly every system in your body. Protein-rich diets have been linked to:
Improved bone density and strength, reducing the risk of fractures.
Better skin, hair, and nail health, thanks to proteins like collagen and keratin.
Enhanced immune function, as proteins are crucial for producing antibodies.
Common High-protein Foods
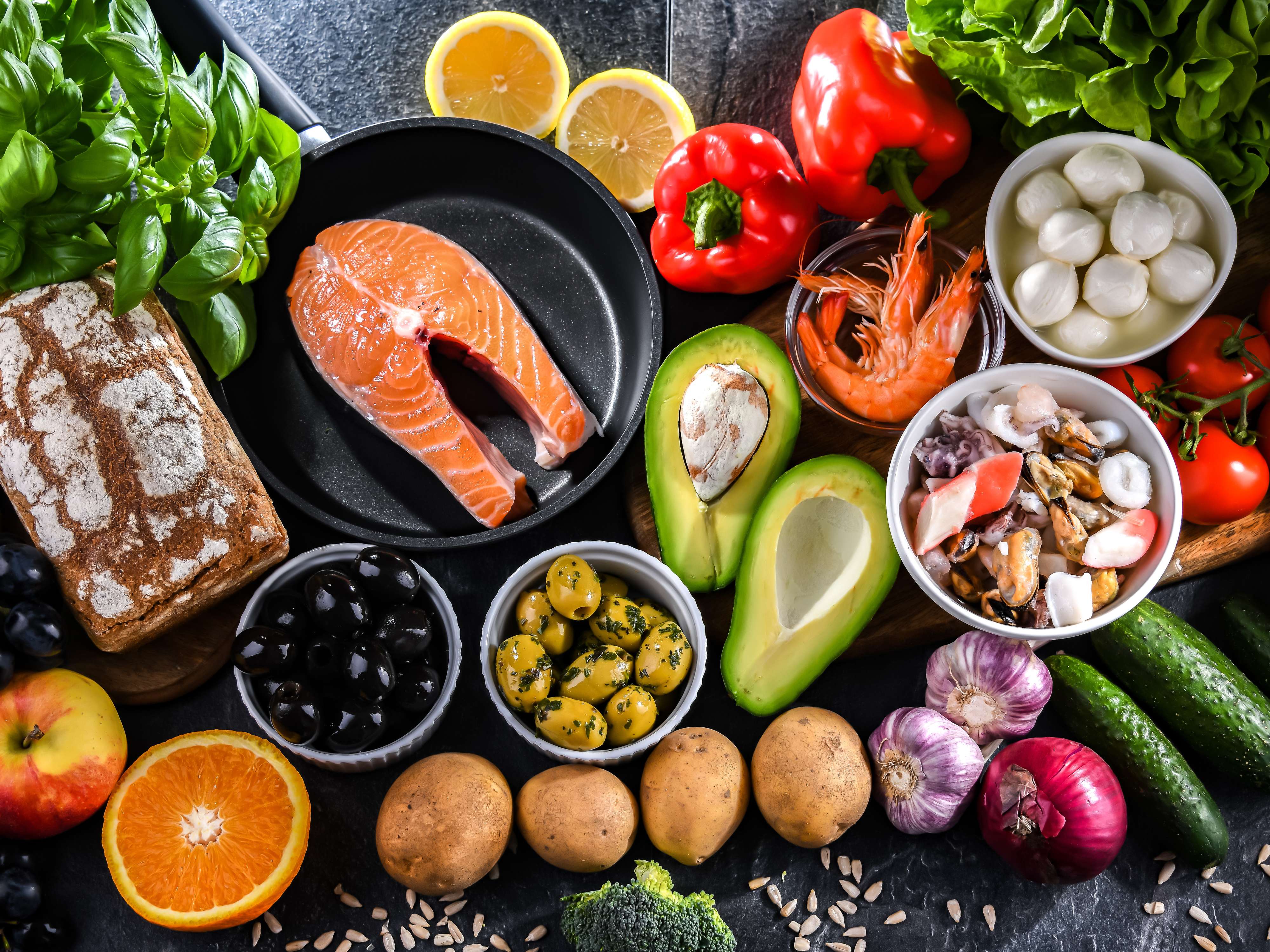

Not sure where to start? Here’s a breakdown of the best foods with high protein to include in your diet.
Animal-based protein sources
Animal-based proteins are some of the most concentrated sources of high-quality protein. They contain all nine essential amino acids, making them a "complete" protein source. Top choices include:
Chicken: Lean, versatile, and packed with protein. A 100g serving of chicken breast delivers around 31g of protein.
Eggs: Nature’s perfect protein package. One egg has about 6g of high-quality protein and plenty of healthy fats.
Fish and Seafood: Options like salmon, tuna, and shrimp are high in protein and rich in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
Dairy: From Greek yoghurt to cottage cheese, dairy products are excellent sources of protein, calcium, and probiotics.
Plant-based protein options

If you’re vegetarian, vegan, or just looking to reduce your meat consumption, there are plenty of plant-based, high-protein foods to explore:
Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are affordable, nutrient-dense, and easy to cook.
Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based staples are incredibly versatile and pack around 10-15g of protein per serving.
Quinoa: A pseudo-grain that’s a complete protein, offering around 8g of protein per cup.
High-protein snacks and alternatives
For busy days or post-workout fuel, keep these on hand:
Protein Bars and Shakes: Convenient, portable, and available in endless flavours.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are great for snacking, with protein and healthy fats.
Edamame: A quick, protein-packed snack with about 18g of protein per cup.
Potential Challenges and Risks
While a high-protein diet has plenty of perks, it’s not without its challenges.
Over-reliance on animal proteins
Consuming too much red or processed meat can increase the risk of certain health problems, such as heart disease or high cholesterol. Diversify your protein sources to include plant-based options for a healthier balance.
Balancing macronutrients
Focusing too much on protein can sometimes lead to neglecting other macronutrients like carbs and fats, which are essential for energy, brain function, and hormone production. Aim for a balanced plate to support overall health.
Kidney and digestive health
High protein intake can strain the kidneys, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions. Additionally, some people may experience digestive issues like bloating or constipation when consuming large amounts of protein, particularly from supplements.
How to Incorporate a High-protein Diet Into Your Lifestyle

Here’s how to make the protein-rich diet work for you:
Planning balanced meals
Build your meals around a protein-rich main, such as grilled salmon or lentil curry, and pair it with whole grains and veggies for a complete, balanced meal.
Meal prep and convenience tips
Batch-cook protein staples like roasted chicken, boiled eggs, or baked tofu at the start of the week. Pre-portion snacks like nuts or protein bars for grab-and-go options.
Adjusting protein intake for your goals
Your protein needs vary depending on your activity level, age, and goals. For muscle building, aim for 0.8-1.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. For general health, 1.2-2.0 grams per kilogram is sufficient.
Is a High-protein Diet Right for You?
The high-protein diet is more than just a fad—it’s a lifestyle choice with proven benefits for building muscles, weight management, and overall well-being. By incorporating diverse, high-protein foods and maintaining a balanced approach, you can harness the power of protein to meet your health goals.
Disclaimer: This information provided is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional advice or guidance. For personalised recommendations or specific concerns, please consult a certified professional.